1、try with catch
还记得这样的代码吗?我们需要手动的关闭资源的流,不然会造成资源泄漏,因为虚拟机无法管理系统资源的关闭,必须手动释放。
public void manualClose(String fileName) {
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
String line;
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fileName));
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
...
}
} catch (Exception e) {
...
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
...
}
}
}
}
骚操作解救你:
public void autoClose(String fileName) {
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fileName))) {
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
...
}
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
}
可以看到,try-with-resources的比前一种方法明显节省了很多代码,资源在try后边的()中生成,在try结束后程序会自动关闭资源。
如果需要声明多个资源,可以在try后面的()中,以;分隔;也就是说,try后边的()可以添加多行语句, 我上篇文章有展示:《保姆系列五》原来JavaIO如此简单,惊呆了
2、instance of
对象是否是这个特定类或者是它的子类的一个实例,返回一个布尔值。左边是对象,右边是类;当对象是右边类或子类所创建对象时,返回true;否则,返回false。
用法:
result = object instanceof class
参数:
Result:布尔类型。
Object:必选项。任意对象表达式。
Class:必选项。任意已定义的对象类。
public interface Monster {
}
public static class Dinosaur implements Monster{
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dinosaur dinosaur = new Dinosaur();
System.out.println(dinosaur instanceof Monster);
}
3、不定项参数 ...
格式如下:
参数个数可以0或者多个
public void method(int...args);
业务场景:
1、在业务开发的时候经常之前写一个方法,但是后来业务变动了,需要增加参数,这个时候可以使用这种方式,多传参数,调用的地方不需要覆盖
2、如果一个方法的的不确定参数个数的情况,通常来说我们会重载,但是如果多了很麻烦,这个时候...可以出场了
//方法重载,解决参数个数不确定问题
public void method(){};
public void method(int i){};
public void method(int i, int j){};
public void method(int i, int j, int k){};
优化之后的形式:
public void method(int i,int ...args);
调用的三种方式
public void call(){
//1、 不使用变参
method(1);
//2、 直接调用
method(1,2,23,4,5,6);
//3、 数组调用
int[] arr = {1,2,23,4,5,6};
method(5,arr);
}
4、跳出多层循环的label
Java 中的标签是为循环设计的,是为了在多重循环中方便的使用 break 和coutinue ,当在循环中使用 break 或 continue 循环时跳到指定的标签处
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
labelA: for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < 5; k++) {
if (k == 1) {
break labelA;
}
System.out.println(1);
}
}
}
}
不推荐这种用法,虽然很骚,但是老老实实的一层一层break 比较好,你觉得呐?
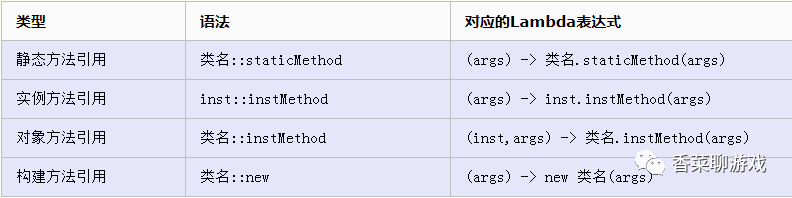
5、方法引用
用Lambda表达式仅仅是调用一些已经存在的方法,除了调用动作外,没有其他任何多余的动作
package org.pdool;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 方法引用测试类
* @author 香菜
*/
public class Trytest {
static List<Player> playerList = new ArrayList<>();
// 静态方法
public static void print(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
static class Player {
private String name;
public Player(String name) {
this.name = name;
playerList.add(this);
}
private void printName() {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> strList = new ArrayList<>();
strList.add("香菜");
strList.add("follow me");
// 1、静态方法引用
strList.forEach(Trytest::print);
// /2、对象方法引用
strList.forEach(System.out::println);
// 3、构造函数
strList.forEach(Player::new);
// 4、对象方法
playerList.forEach(Player::printName);
}
}
总结:
1、在try结束后程序会自动关闭资源
2、instance of 必须是子类
3、参数个数可以0或者多个,重构代码利器
4、使用 break 或 continue 循环时跳到指定的标签处
5、方法调用是除了调用动作外,没有其他任何多余的动作
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能给你带来帮助,也希望您能够多多关注好代码网的更多内容!